How to prepare for the CT examination
What is CT Topometry?
CT topometry (Computer Tomography) is used in radiotherapy for precise planning and execution of radiation treatment. It helps specialists accurately determine the location of tumors and surrounding tissues, which is crucial for directing radiation to the target area while minimizing the risk of damage to healthy tissues.
Key aspects of CT topometry in radiotherapy:
1. Patient positioning accuracy:
CT topometry allows for detailed examination of the patient's anatomy in three planes and enables precise positioning of the patient on the radiotherapy treatment table. This is essential for ensuring reproducibility of the patient's position during each treatment session. CT topometry helps create patient positioning maps, allowing for accurate radiation targeting. Special markers (such as tattoos or markers) may be used when necessary, which assist in repositioning the patient accurately during each radiation session.
2. Treatment planning process:
CT is used to create a 3D model that allows for precise localization of the tumor, as well as evaluation of the position of important organs and tissues. This helps reduce the risk of damage to healthy structures.
3. Use during treatment:
CT topometry is often employed during radiotherapy to refine patient positioning and monitor changes in the body (for example, changes in tumor size, patient weight, or organ shifts). In some cases, organs such as the lungs, heart, or intestines may move during breathing or other physiological processes. CT topometry can be used to analyze these movements and adjust radiation plans accordingly, which is particularly important for tumors located in the chest or abdominal cavity.
4. Visual planning and dose distribution:
CT images are used to create radiation plans that ensure precise dose distribution based on the characteristics of the tumor and surrounding tissues. This allows for treatment with minimal side effects.
5. Reducing complications:
By using CT topometry for precise planning, it is possible to reduce the radiation dose to healthy tissues, thereby minimizing the risk of side effects and complications, as the radiation dose is directed only at the tumor.
Overall, CT topometry is a crucial component of radiotherapy that enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of radiation treatment. It ensures maximum impact on the tumor while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Diet – the day before the examination
1-2 days before the examination, exclude foods that may increase gas production in the intestine
- Apples, pears, mangoes, peaches, plums, watermelon, cherries
- Onions, garlic, asparagus
- Legumes, mushrooms
- Cabbage (including sauerkraut), broccoli
- Rye bread, corn, crackers
- Beer and other alcoholic beverages
- Carbonated drinks
- Honey, sugar substitutes (including chewing gum)
- Fruit juices
Foods that reduce gas formation in the intestines:
- Free of lactose / rolled oats / rice milk
- Buckwheat porridge, rice
- Boiled meat
- Eggs
- Fruit jelly
It is important to follow these recommendations, as gas accumulation in the intestines can enhance intestinal peristalsis (movement), which in turn worsens the visibility of pelvic organs during the examination.
Diet – on the day of the examination
It is not recommended to come for the examination on an empty stomach, as this can increase intestinal peristalsis. A light breakfast is advised.
• To take the following medication:
- Espumisan: 2 tablets 3 times a day, the day before and on the morning of the examination.
- No-spa 40 mg (ordinary): 3 tablets a day, 30 minutes before the CT topometry, regardless of food intake.
• Regarding bowel emptying:
- In the clinic, under the supervision of medical staff, a micro-enema (Microlax) will be administered. For this procedure, please arrive at the clinic 45 minutes before your scheduled examination time.
• Bladder preparation:
- Upon arrival for the CT topometry, inform the medical staff about the fullness of your bladder so that, if necessary, you will receive further instructions (whether to continue filling the bladder, empty the bladder, continue drinking liquids, etc.). Do not empty your bladder without informing the medical staff.
• Bowel contrast preparation:
- Omnipaque 25 ml should be dissolved in 1 liter of (non-carbonated) water.
The prepared solution should be consumed as follows:
-The evening before the CT examination.
- On the morning of the CT examination.
- 30 minutes before the CT examination in the hospital.
It is recommended to drink the solution slowly, in small sips or using a straw, to avoid swallowing air.
Other news

Year in Review Medical Tourism
Read more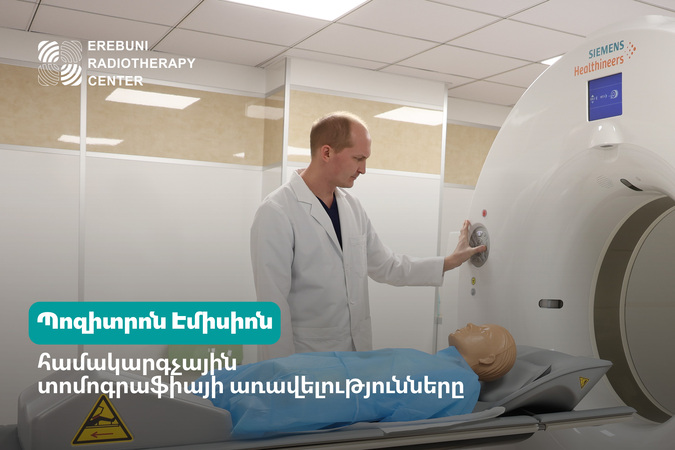
Differences and advantages of Positron emission tomography and computed tomography (PET-CT) compared to other radiological methods
Read more
New methods of lung cancer treatment
Read more
The stages of radiation therapy
Read more
A New Beginning at the “Erebouni” Radiotherapy Center
Read more
Delegation from Sochi Visits Erebuni Radiotherapy Center
Read more

